SaaS Factory
Mavengigs
Mavengigs is a global consulting firm providing consulting services for Mergers & Integrations (M&A) and Transformations. Through our network of independent resources and partners, we serve clients in USA and Europe. Mavengigs is a division of Panvisage Inc. (a holding company with interests in consulting, education, real estate and investments).
SaaS Factory
SaaS Factory is Mavengigs’ global delivery model for software development services where our Mentors (thought leaders) and our Mavens (Experts) collaborate seamlessly across time zones, geographies and organizational boundaries, based on standards (tools and processes) to innovate at speed and scale and turbocharge your transformations.
SaaS Factory provides additional capacity to deliver fast transformations by collaborating based on well-defined product delivery standards and tools for efficient delivery.
Any scenario that requires rapid transformation delivery is a business driver for SaaS factory. Due to a fast-changing business environment, there is a growing ‘alignment gap’ between business requirements and IT delivery. Significant disruptions are being caused by the advent of generative AI. Typical M&A projects (integrations or divestitures) are not enough to achieve target value, requiring additional rapid transformations for extra ROI. Numerous scenarios stand to gain significant advantages from SaaS factory.
Software Development as a Service (SDaaS)
SaaS Factory is really about Software Development as a Service (SDaaS) to deliver specific innovative products required for your business transformation.
Leadership sets the mission and vision and approves funding. Organizations must respond quickly and efficiently to create value. Software plays a crucial role, serving to optimize tasks, increase profits, reduce costs, minimize time to market, and increase strategic competitiveness. SDaaS is based on context rather than control. One key aspect of this model is Continuous Compliance. SDaaS ensures that solution delivery mission is met with quality and security embedded at the onset.
SDaaS is a combination of platform (software assets, tools, processes) and resources (highly motivated and skilled SMEs) that expedite the production and delivery of software development. Well defined tools, technologies and processes reduce waste by eliminating redundant activities, minimize unnecessary tasks and reduce training time, resulting in shorter time to market and reduced development costs. Automation, connecting people, process, and technologies, delivers a high functioning pipeline to deliver software. Using SDaaS over several months can change values, attitudes, and culture of the organization.
Software Development as a Service model (SDaaS) will enable to build a solution baseline once – for repeatable use. The goal is to achieve:
- Lower Lead Time, Increase deployment frequency
- Lower MTTR (Mean Time to Repair)
- Lower change/fail rate
- Increase mission capabilities
- Automation of Repeatable Tasks
- Freeing Up Time for mission critical work
- Meet Rapid demand for quality solution
SDaaS will minimizes the worry about basic and often redundant components of an application like
- Authentication
- Systems Design
- Deployment platforms
- Standardization
- Administration
Benefit of this Software Development as a Service model (SDaaS) are:
- It will help enables innovation
- It will reduce complexity and time
- Improve Time to Market
- Institute Governance processes and policies
- Address security and threat
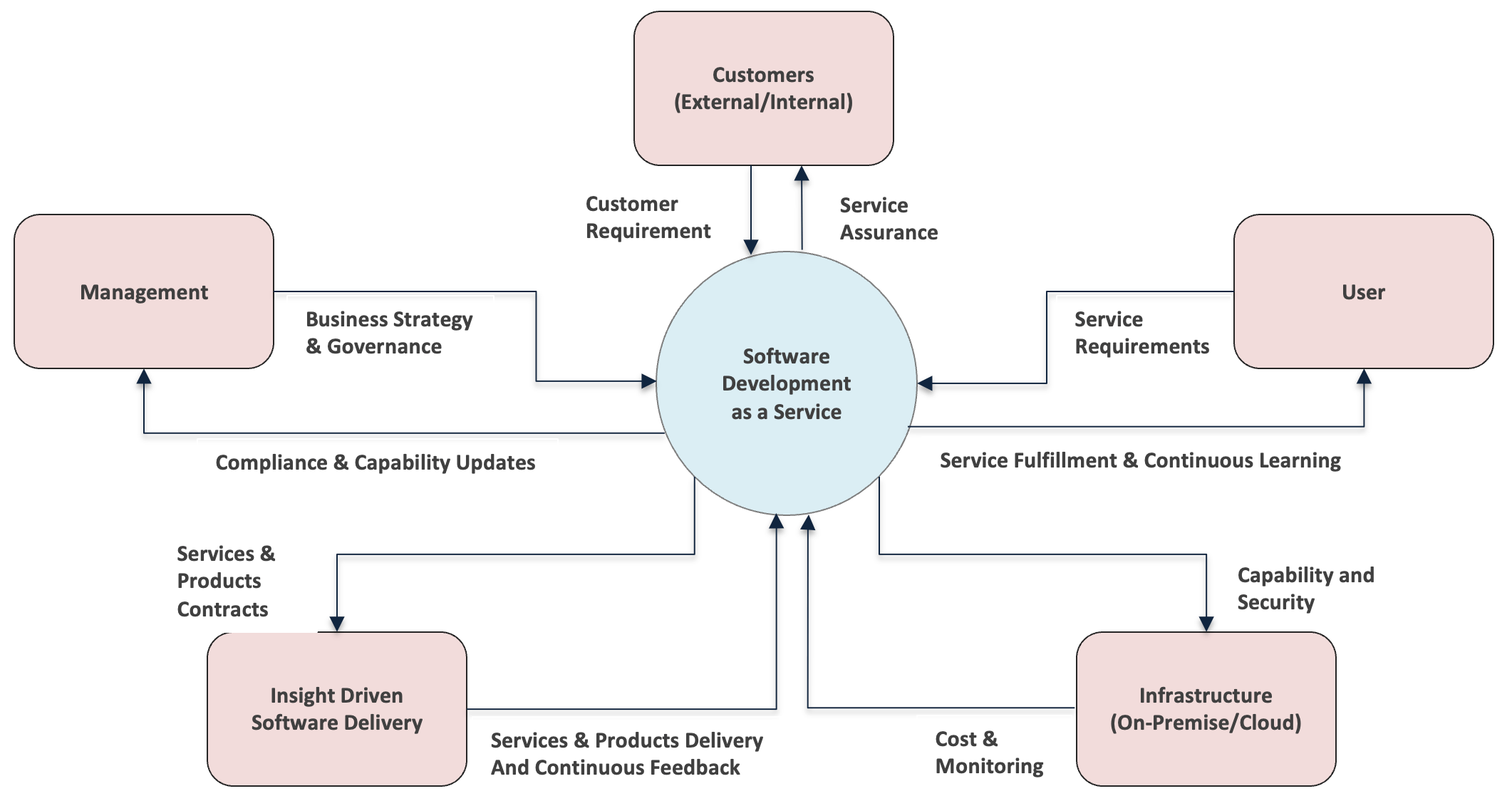
The reference model defines a comprehensive set of activities that enables effective collaboration of IT within an Organization. The key components being:
Customer
They can be external or internal whose problem we are trying to solve, or requirements are to be/being addressed. The objective is to pinpoint the disparity between the existing condition (the problem) and the intended condition (the goal) of a process or product.
Management
The Management is responsible for providing the business strategy, governance, and architecture. Value creation along with continuous compliance are the key objectives.
User
The user community provides feedback, utilizes self-service, and generates service requests. Empowering users and instituting continuous learning is the strategic goal.
Infrastructure
Infrastructure requirements relates to various environments, tools, software, storage, CPUs etc. Cost management, Monitoring and Security are the key aspects of Infrastructure.
Insight Driven Solution Delivery
Delivery driven by insights provides thorough analyses sourced from commonly used continuous integration and continuous delivery tools, with the goal of improving the speed, quality, and control of applications. By gathering and examining results from unit tests, functional tests, and code coverage tools, Insights evaluates whether the code adheres to predefined policies established at specific stages in the deployment process. If the code falls short of meeting a policy, the deployment is stopped, averting potential risks from being introduced. The presence of insights can act as a protective layer within the continuous delivery environment or as a method to institute and refine quality standards.
Continuous Delivery
Continuous Delivery empowers development teams to automate the progression of software through the software development lifecycle, offering numerous advantages when deploying in an integrated environment. These include:
- Reducing time to deployment: Achieved through continuous testing and development.
- Decreasing costs: Particularly those linked to traditional software development methods.
- Scaling software development: Adaptable to the size and scope of the project.
- Automatically deploying code: Ensuring seamless integration into each phase of the development cycle.
Continuous Feedback
Continuous Feedback plays a crucial role in optimizing delivery processes. Although tools can facilitate feedback loops, teams must actively work to minimize unnecessary noise and consistently measure success. The establishment of a continuous feedback loop is realized through Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD), and the effectiveness of CI/CD relies on an ongoing cycle of feedback. Importantly, continuous feedback isn’t confined to the software development process; rather, it necessitates coordination among teams across code development, deployment, support, and even in non-IT functions like business process flows. To implement continuous feedback successfully, it is vital to fine-tune the CI/CD pipeline and formulate a strategy to address the inherent challenges within feedback loops.
Continuous Learning
A culture of Continuous Learning is essential for staying relevant and achieving success. This culture is one of empowerment, achieved by fostering a growth mindset, actively pursuing learning opportunities, and instilling a learning culture within teams. It stands as a vital element in any successful business transformation strategy, involving employees to consistently enhance their skills, knowledge, and competencies. This approach enables an organization to remain competitive and adapt to the rapidly changing business environment.
SDaaS Framework
Software Development as a Service (SDaaS) framework is based on DevOps / AI-ML Ops as the key operating model along with the adoption of ITIL 4 principles, Lean Best Practices and Governance principals, processes & policies.
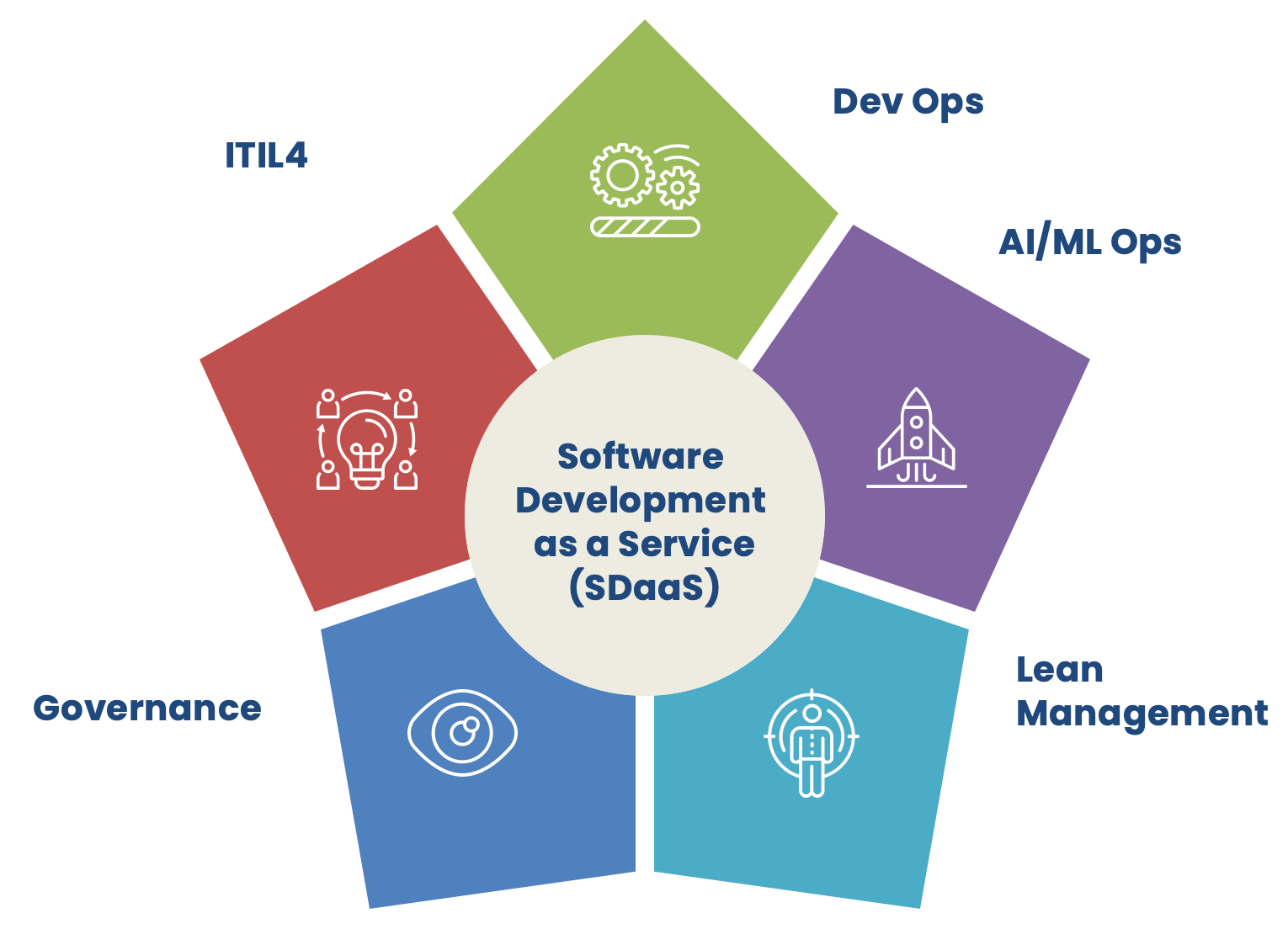
(a) ITIL 4 Principals
The seven principals of ITIL 4 adopted in this model include:
1. Focus on Value
Focus on value principals of stakeholders including experience of customer and users. Ensure Stakeholder’s commitment, scope is realistic with definitive and achievable expectations.
2. Start where you are
Analyze the existing state and leverage & improve all available services, processes, programs, project, and people for the desired outcome.
3. Progress Iteratively with Feedback
Breakdown the work into small iterative deliverables or tasks. It is better managed and executed in timely fashion while maintaining focus on the effort. Use Feedback to identify the issues, risks, and opportunities.
4. Collaborate and Promote Visibility
Better collaboration and teamwork among all stakeholders will result in greater buy-ins, information & knowledge sharing, understanding and trust building. This enables better success in achieving the objectives and long-term success.
5. Think and Work Holistically
The mission of delivery should be service oriented. Efficient and effective delivery of results to both internal and external customers hinge on the dynamic integration and adept management in a collaborative environment to dispel any form of hindrance or disruption. Coordination is essential to offer a clearly defined and valuable outcome.
6. Keep it Simple and Practical
Use the minimum number of steps necessary to accomplish the objective(s) and eliminate all noise. Simplify the process and adopt an outcome-based thinking to define practical solutions that deliver results.
7. Optimize and Automate
Optimize a process or a workflow and then automate. Define the processes/workflows that need to be manually manages and which can be automated to improve efficiency and reduce cost
(b) Lean Management
Embracing Lean Management principles is aimed at fostering improved workflow and cultivating a culture of continuous improvement in cycle of delivery. The goal is to in still a commitment to quality, enhance value creation, minimize costs, and elevate overall performance.
(c) Governance
The governance principals adopted in the Software Development as a Service (SDaaS) Model are as follows:
- Define and have clarity in roles, responsibilities, policies, and standards for effective Modern Management
- Prioritize areas like data quality, security, and compliance.
- Provide the necessary framework, processes, and guidelines for managing and ensuring the quality, integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data.
- Enforce data standards and policies and facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Enhances collaboration among stewards from various departments to achieve data governance goals.
- Ensuring protection, fairness, ethics, responsibility, and transparency
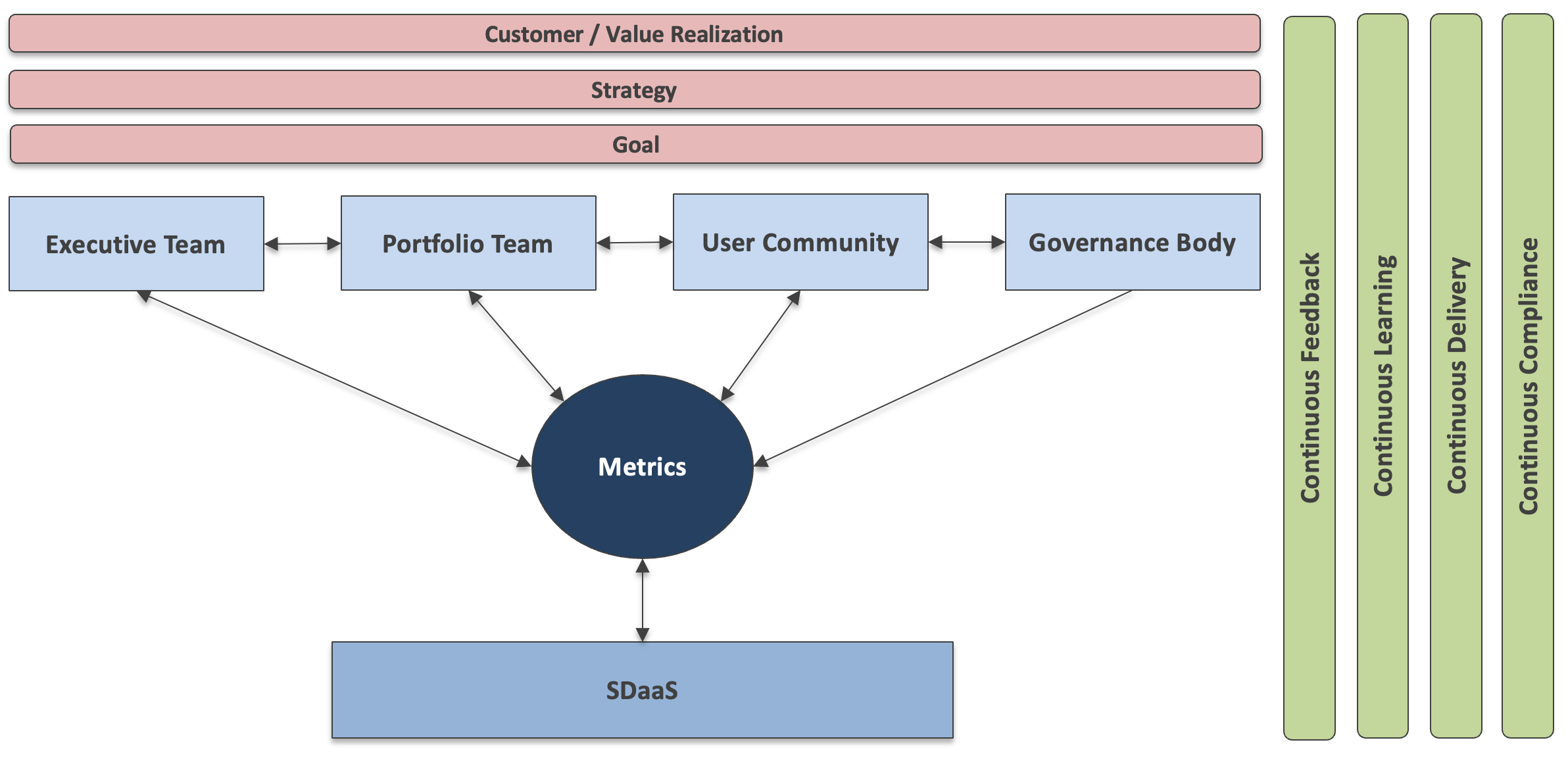
(d) Mavengigs Operating Model
Mavengigs’ SDaaS (Software Development as a Service) operating model cultivates a Generative culture that is performance-oriented, proactive, and prioritizes collaboration to ensure the timely dissemination of information to the right individuals, with a strong emphasis on value creation to achieve organizational goals and missions. In Generative cultures:
- Information and knowledge are actively shared.
- Failures involve analysis and inquiry rather than blame or finger-pointing.
- Shared responsibility is emphasized.
- Collaboration between teams is both encouraged and rewarded.
- New ideas are welcomed rather than discouraged or suppressed
SDaaS (Software Development as a Service) introduces a novel approach where standardized rules, varying levels of commitment, transparency, risk, and complexity are shared across all teams. Embracing a lean approach to management and governance, it emphasizes collaborative efforts among different teams. The key focus lies on measurable metrics that signify gains in customer and service value. This approach enables organizations to witness tangible successes, fostering support for change, promoting continuous learning, and empowering the user community.
Strategic goals drive the definition of portfolios, which in turn guides software product development. Within the Portfolio team, a crucial aspect is to establish the measure of Return on Investment (ROI), leading to agreed-upon metrics. The team observes product development and assesses its alignment with the target state. Their responsibility extends to ensuring a clear, shared understanding of what success looks like and fostering a sense of responsibility in achieving the overarching goals.
The governance body ensures comprehensive representation across various functions, ensuring visibility, feedback, and open discussions. The cross-functional representation of stewards within this structure guarantees the removal of barriers and fosters effective teamwork.
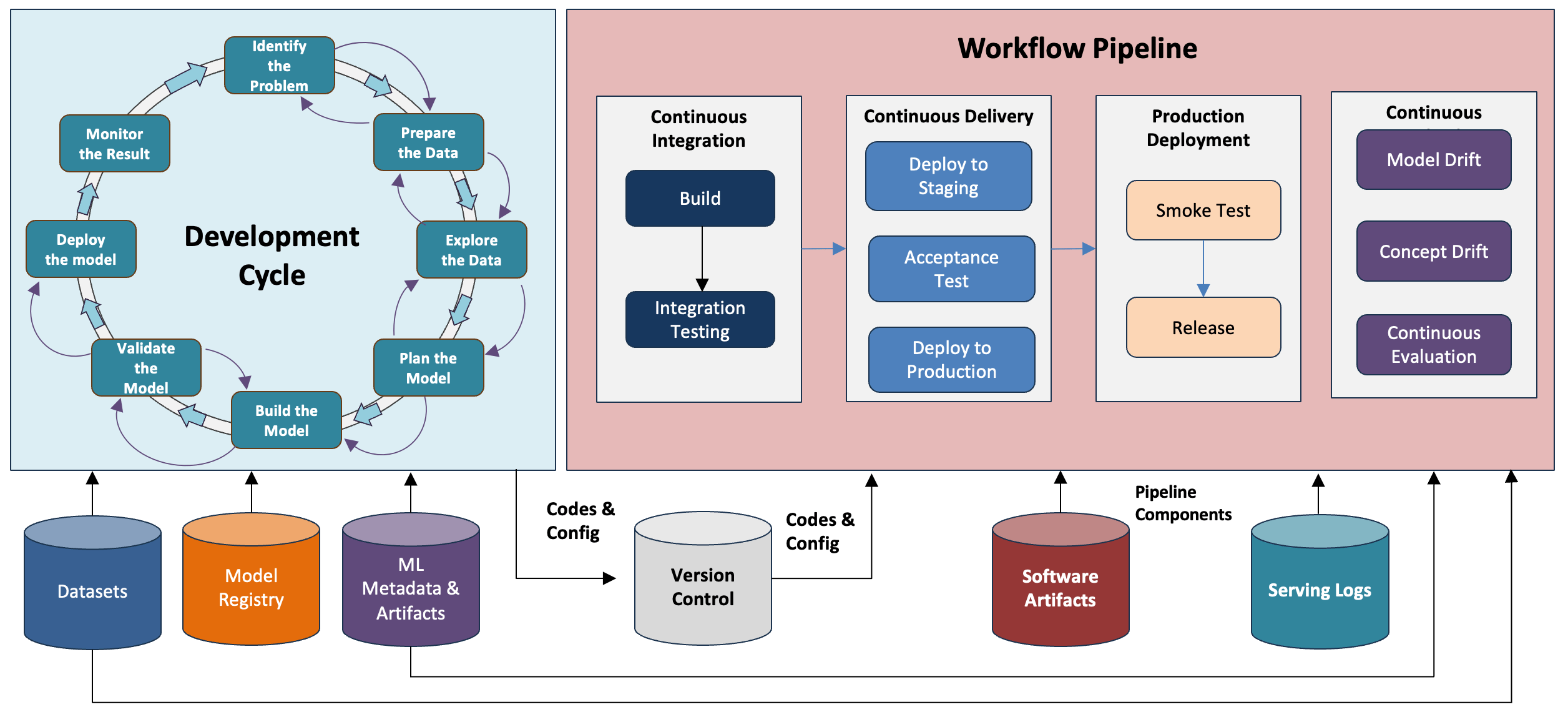
Solution Baseline – Repeatable Use
Mavengigs’ SDaaS (Software Development as a Service) ensures the consistent and repeatable utilization of various application-building underlying components. The diagram above illustrates a microservices-based architecture using the widely employed Kubernetes. The emphasis is on shared responsibility, wherein the Mavengig’s team collaborates with the client team to deliver timely and cost-effective solutions.
This approach can be used for any application development including AI/ML based solutions.

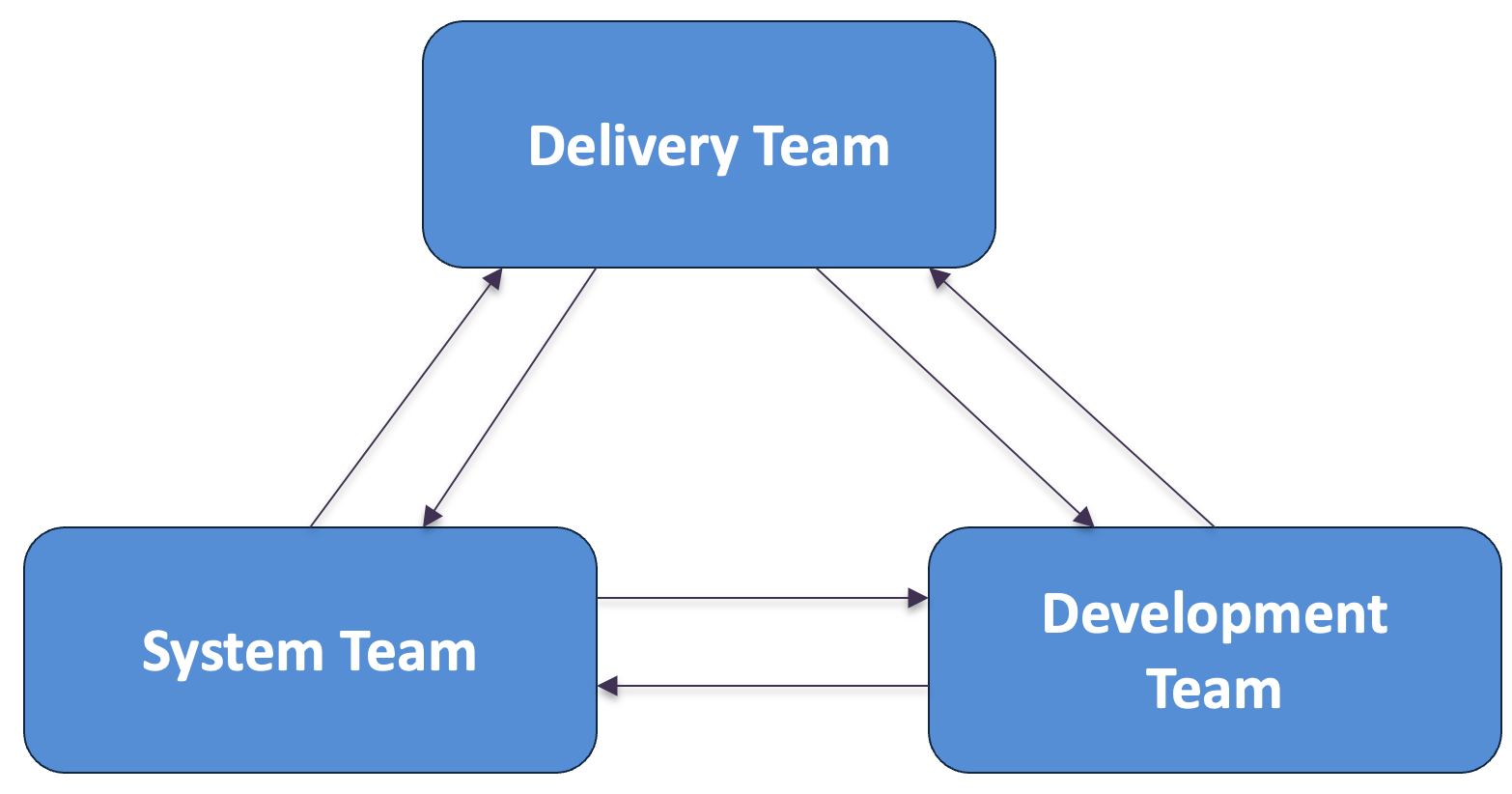
Mavengigs is focused to build a customer centric experience to best support the emerging needs of users. The teams are categorized into 3 major responsibilities:
Delivery Team
They are the client facing team. They will be responsible towards value creation, continuous learning, team collaboration and knowledge sharing. They are primarily responsible for working with User communities and customer stakeholders to define and implement the strategy, governance, architecture, program management and administration. They will responsible and will lead other teams in defining the scope, value creation and value realization.
Development Team
The development team will be responsible towards continuous integration for building, testing, and enhancing the reusable libraries related to process, codes and best practices. They will oversee the repository. They will align themselves with the delivery team on matters related story boarding, backlogs, and sprint cycle. They will be responsible in managing the sprint cycle and change management processes.
System Team
The system team will be responsible for continuous delivery and will manage the infrastructure and security of the environments using standard tools and accelerators (in consultation with the Architecture and Security leadership). They will ensure the establishment of common pipelines and automate processes and workflows. They will monitor the system and will provide support towards managed services and incident management. They will provide continuous feedback to the Delivery team. One primary responsibility is deploying and maintaining the repeatable reusable components.
Both the development and system teams feed the delivery team producing a high-volume factory of products, services and solutions.
SDaaS Methodology
The SDaaS methodology adopts DevOps & Agile delivery as an iterative software development approach emphasizing collaboration, rapid software releases, and customer feedback. It serves as both a cultural and management philosophy, striving to engage every team member in continuous improvement and value creation to customers.
SDaaS delivery approach is designed to eliminate silos between development and operations teams. Teams leverage tools and practices to automate processes like code deployment or infrastructure provisioning, enabling organizations to swiftly deliver applications and services.
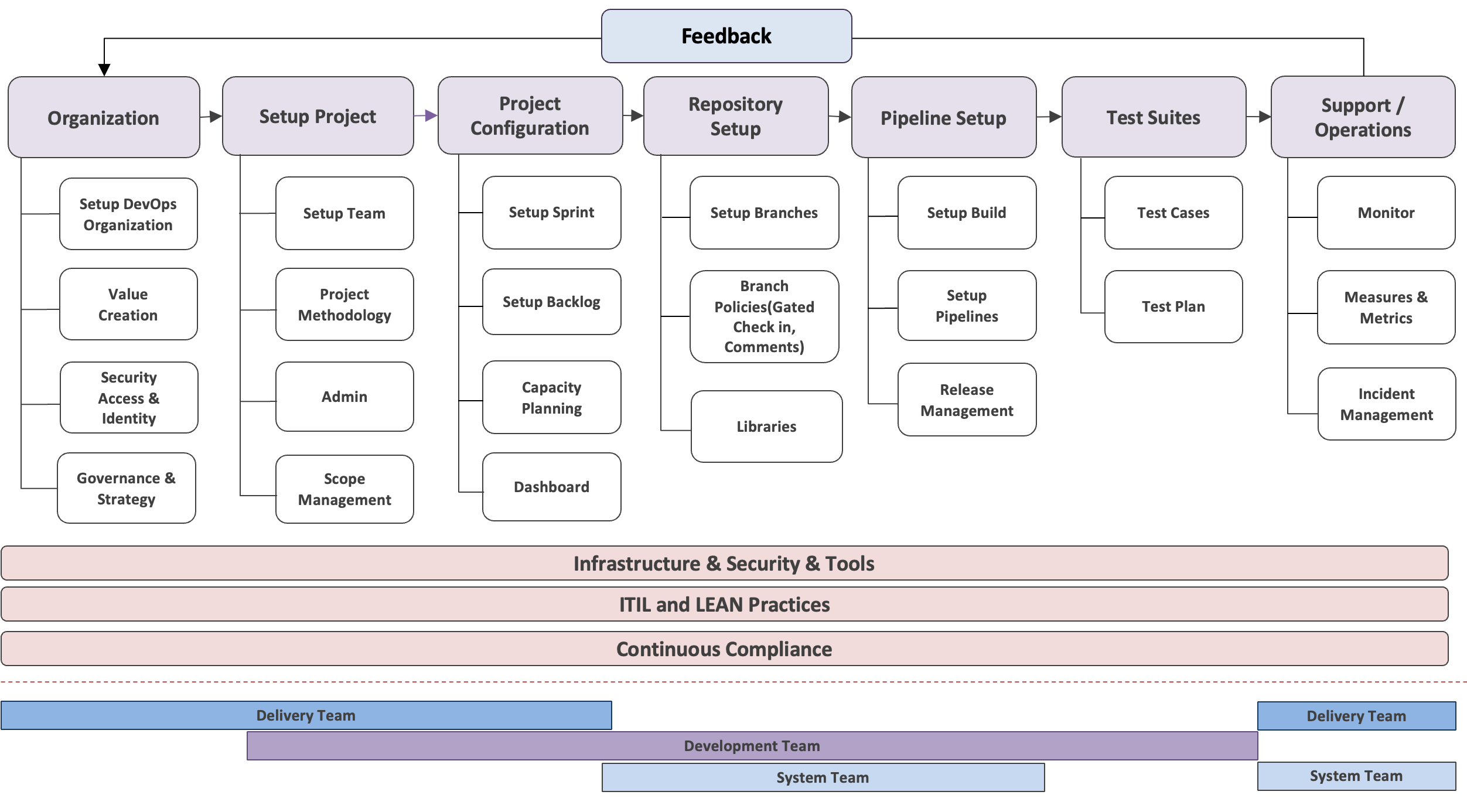
This delivery structure is designed to foster collaboration, efficiency, and continuous improvement. It encourages teams to implement enhancements, collaborate effectively, and minimize bottlenecks using feedback loops to continually improve work deliverables. This approach ensures an accelerated development cycle while upholding quality standards and maximizing efficiency by adhering to lean principles.
Best Practices
The team places a special emphasis on testing to guarantee the reliability and high quality of the work product. This involves maintaining a focus on testing code changes at the earliest stages to detect issues promptly. The testing procedures encompass unit tests, functional tests, performance tests, acceptance testing, and integration testing. The continuous integration process ensures that codes are regularly merged into a shared repository, enforcing the testing of codes at consistent intervals. This approach aims to enhance the overall quality and reliability of the developed software.
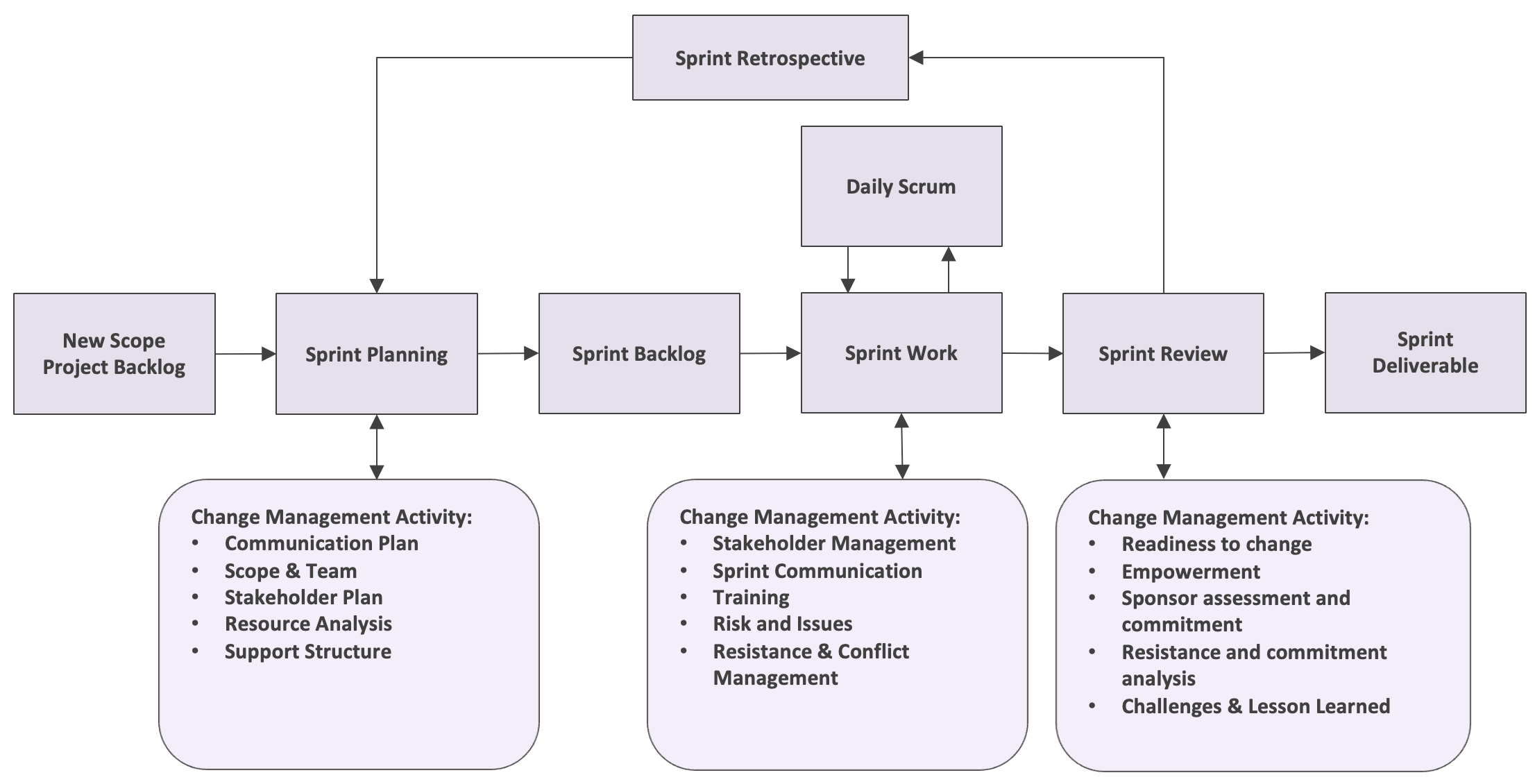
Teams adopt an iterative approach, making incremental changes to enhance a product while fostering a culture of learning, growth, and continuous improvement. This involves implementing Scrum practices, such as retrospectives, to actively promote a culture of refinement. Additionally, teams focus on monitoring various aspects, including application performance and health, infrastructure, conducting post-incident reviews, and analysing data through incident management. These processes aim to identify areas of improvement and contribute to the ongoing enhancement of the team’s performance and the overall quality of the product.
Automating the process of building, testing, and deploying will be utilized as extensively as possible to facilitate the frequent release of new versions of work products. This approach is geared towards reducing costs and achieving just-in-time delivery, streamlining the development and release cycle through efficient automation.
Version control will establish the practice of managing code in different versions, facilitating the tracking of revisions and change history. This ensures that the code is easily reviewable and allows for efficient recovery of previous versions when needed.
The utilization of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) will involve deploying system resources in a reliable, repeatable, and controlled manner. This approach enables the automation of infrastructure provisioning and configuration through code, ensuring consistency and efficiency in deployment processes.
Conclusion
SDaaS (Software Development as a Service) offers flexible scalability, substantially reducing the time required for changes and increasing deployment frequency. This, in turn, enhances project Return on Investment (ROI) within a governed working environment. SDaaS promotes a metrics-based lean approach in a collaborative environment centered around responsibility. The focus is on the timely delivery of value-based solutions, fostering knowledge sharing, and facilitating change adoption.
Please contact us today!
Mavengigs
16192 Coastal Highway, Lewes, DE 19958
Contact Us
Ph: (310) 694-4750, sales@mavengigs.com
Los Angeles
San Francisco
Chicago
New Delhi